In a new world where healthcare systems need to be of the highest order, the processes have taken a strong momentum to improve infrastructure and amenities following the pandemic years. The policies are rapidly resurfacing as they have become crucial for the citizens of a country.
Hospital Security involves securing patients, staff, visitors, and physical infrastructure. Hospitals have multiple access points and witness huge crowds daily. Most hospitals are considered ‘soft targets’ as they are high-density locations including crowded areas such as schools, shopping malls, and schools. They commonly have many access points with limited security guards. Even
the threats of theft, violence and other crimes are real risks for hospitals. These are some of the common reasons why we may be more vulnerable to certain types of security risks in the coming future if left unattended.
In the face of a pandemic, risks are heightened, and the need for stricter security norms looms large. The role of hospital security is to ensure the safety, security, and welfare of all patients, staff, and visitors to their full capacity. Apart from people, it is also important to secure medical equipment, operating rooms, facilities, and sensitive information. Without adequate safety and security measures, hospitals can become easy targets for intrusion and unwarranted activities.
Statistics
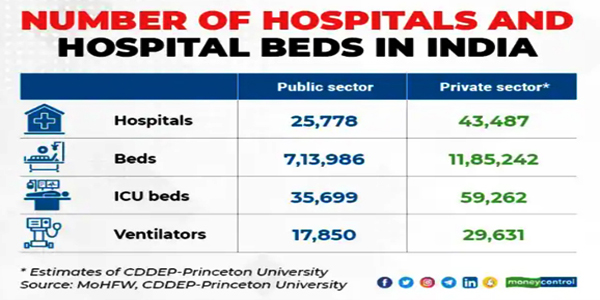
There are a total of 18,99,228 hospital beds in India, out of which 11,85,242 are in the private sector, and the remaining 7,13,986 are in the government sector. 59,262 ICU beds are in the private sector and 35,699 beds in the public sector. (April 2020, analysis by the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy).
The Union Budget of 2022-23 allocated INR86,200 Cr. to the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, a nearly 16% increase in comparison to FY 2020-21.
By 2036, the population of India is expected to increase to 151.8 crores (approx.) at the rate of 1.0 percent annually. Calls for better infrastructural facilities.
Types of Hospital Safety
Patient and child safety, emergency services, contract staff, catering establishments, parking traffic, pharmacy control, clinical safety, equipment protection, fire safety, and evacuation.
Risks & Security Threats
The healthcare industry is widely regarded as having a weak security system. The main challenges that arise in hospital security are:
- Deficiency in manpower and infrastructure.
- Unchecked visitors due to heavy traffic at the entry and exit gates is one of the probable risks.
- The parking area is a hot spot that needs immediate attention for threat control, as the damages may result in an expensive disaster.
- Healthcare data breaches and cyber-attacks expose highly sensitive and valuable information of patients.
- In 2016, a kidney trafficking racket was wedged in Mumbai’s hospital meanwhile Delhi faced an incident that includes the swapping of newborn babies due to gender biases in 2017. The year 2022 recorded an unpleasant episode where some of the relatives ransacked a private hospital in Nagpur and further assaulted a doctor after the patient’s death.
These are some of the issues that are confronted by hospitals every day, and the number of such incidents per year is increasing. If we tighten our security systems, it may reduce the scope of these cases significantly. Together with manned guarding, vigilance, surveillance, and electronic security can such threats be addressed better.
Safety Measures
- Maintenance of the records and medical history of all patients as credible National Health Data is important for the govt, and stakeholders, and to also maintain transparency with the democratic citizens of this country.
- Provisions by regulatory authorities, planned strategy, patrolling and reporting, quick response teams (QRTs), protection of high-value laboratories, allotting of investigation officers, more organized and categorically strict ‘entry & exit’ systems, easing out language barriers, and reduction of cues, monitoring, and checking of cue reduction besides registration of all visitors.
- Electronic access systems for physical security needs like printing photo ID access cards and face recognition systems for the authorized staff, and visitors.
- Biometric authentication such as fingerprints, upgraded software integrations, high-speed internet access, 24×7 control room regulation, and automatic door controllers with a magnetic locking system.
- Disease control/ prevention, administrative security, and safeguarding of dormitories having high-risk equipment and inflammable tools.
- Reliable and latest information on healthcare resources and their deployment can address problems with real-time solutions. To further ensure a district-level electronic database of information on health system components.
- Hospital staff & security coordination training, fire training, and security guards training to counter any mishaps for real-time action control.
- Verification of IDs and badges to make sure the doctors, patients, and visitors are at their assigned wards. Furthermore, contactless access card readers for easy access.
- Effective communication amongst security officers, quick monitorization of strategically positioned CCTV cameras. Metal detectors and screening tests of all visitors.
- Handling the patient’s and their relative’s emotions in cases of serious medical issues. Besides the doctor, a skilled healthcare security officer can maintain composure and tactically handle the emotions of the deceased/ injured.
- Patrolling by the trained security officers for potential fire threats due to sparks generated via electrical equipment or combustible materials. Regularly examine the expiration dates of the fire extinguishers. Further reporting the issue to the firefighters.
- Abduction of infants, inmate escapes, drug theft, and even gun violence are some of the crimes committed in hospitals. These crimes can be avoided by a strong and effective security system to avoid these crimes.
- Establish integrated health information Exchanges, architecture, and national health information networks.
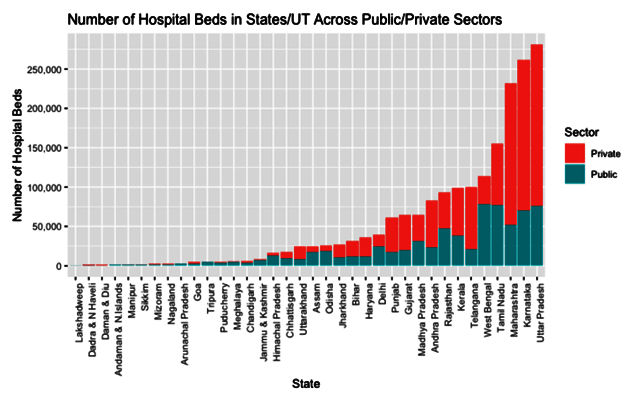
The year 2020 recorded the concentration of most ventilators and hospital beds in India and found seven states that topped the charts. Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Telangana, and Kerala. Amongst which the highest number was recorded in UP (as shown in the previous page). Although the dynamics have changed now with an increase in the number of hospital beds and ventilators over the years.
Besides taking these necessary steps; the latest tools and technology are the requirement of the emerging healthcare sector. To detect and protect people from waste, and acquired infections, systematic management systems, information systems, establishing hospital committees, planned committees, infrastructure and policies, adequate amount of and optimal utilization of resources, risk management, and security guards.
Hospital security and healthcare are matters of national pride. India stands at rank 66 of 195 countries in the 2021 Global Health Security Index, which demonstrates the pre-preparedness of a country for an epidemic or pandemic in the coming future. Ergo, the healthcare systems have a social and national responsibility as a body to minimize the risk of threats.
Safety should be the last concern for a patient or a visitor entering the hospital premises. Proper security protocols and alert security staff can minimize damage in the face of an emergency and otherwise. The benefits of proper security at a hospital are significant and can go a long way in establishing the reputation of a hospital.



